Curriculum Vitae
PERSONAL DATA

| Name |
Ruben Zamar |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Affiliation |
Professor of Statistics |
|
University of British Columbia |
|
|
| Address |
Department of Statistics, UBC |
|
3182 Earth Sciences Building |
|
2207 Main Mall |
|
Vancouver, BC |
|
CANADA - V6T 1Z4 |
|
|
| E-mail |
ruben at stat.ubc.ca |
|
|
| URL |
http://www.stat.ubc.ca/~ruben/website |
|
|
|
|
|
| Degree |
Institution |
Subject Area |
Date |
Country |
|
|
|
|
|
| Public Accountant |
Univ. de Cordoba |
Economics |
1973 |
Argentina |
|
|
|
|
|
| M.Sc. |
CIENES |
Statistics |
1977 |
Chile |
|
|
|
|
|
| M.Sc. |
Univ. de Pernambuco |
Mathematics |
1981 |
Brazil |
|
|
|
|
|
| Ph.D. |
University of Washington |
Statistics |
1985 |
U.S.A. |
RESEARCH

1. Areas of main research interest

- Data mining and text mining
- Data quality
- New robust procedures
- Statistical computing
- Bioinformatics


2. Main Contributions to the Theory of
Robustness

At the beginning of my research career in 1986 I was mainly interested in the general
theory of quantitative robustness, which was dominated by the concepts of influence
function and breakdown point. I thought that these measures of quantitative robustness
gave an incomplete assessment of the degree of robustness of an estimate. I also thought
that a much better assessment can be made using the concept of maximum asymptotic bias
(maxbias) introduced, for the simple location model by Huber (1964). Huber quickly
abandoned this approach because it, in his opinion, led to a "rather uneventful
theory". The maxbias approach was "dormant" for nearly 20 years until I
showed in my Ph.D. dissertation that maxbias functions and minimax bias estimates can be
derived for other models including scale, regression and orthogonal regression. Together
with collaborators (Victor J. Yohai and R. Doug Martin) we showed that the minimax bias
theory can be extended to linear regression and found minimax bias robust regression
estimates. It is safe to say that today the maxbias approach is considered the most
important theoretical tool in quantitative robustness. My current work on this area is
aimed at showing that the maxbias approach can also give rise to useful statistical
procedures, via the construction of bias bounds and globally robust inference. I wish to
create and popularize inferential procedures which take into account the possible effect
of contamination bias. Together with collaborators (V.J. Yohai, J. Adrover, J.R.
Berrendero and M. Salibian) we developed a new globally robust confidence intervals of
minimax length and initiated the new robustness theory which we call "global robust inference". The aim of global robust inference is to
construct robust confidence intervals, p-values and tests that take into account not only
the uncertainty due to "normal" data variability but also the bias effect of
"abnormal" noise and poor data quality.

3. Current Research Interest and
Directions

I am currently mostly interested in data mining and statistical computing and pursue a
fruitful collaboration with researchers in Computer Science including Raymond Ng, Alan
Wagner and Laks Lakshmanan. We are co-supervising several graduate students who are
working on different data mining problems. A paper that resulted from this collaboration
won the "Best Paper Award" in the KDD 2001 Conference. We are now working on the
scaling of robust algorithms using parallel computing, on text mining and compression of
large relational databases. Another main achievement from this collaboration is the three
year funding (2001/2003) obtained from MITACS for the project "Toward Interactive
Data Mining". Our MITACS project had two main industrial partners: Insightful
Corporation (the producer of Splus and I Miner) and IBM through a collaboration with the
iCAPTURE Centre at the St Paul's Hospital.
I am also interested in the study and modelling of data quality in the context of
large, high dimensional datasets. Together with my former student, Fatemah Alqallaf, we
proposed a new, flexible model to represent contamination in multivariate data. This model
provides a mathematical formulation for a phenomenon that we call "outlier
propagation". I think that outlier propagation is a serious statistical problem and
that our model may become an important tool in the context of the robust analysis of high
dimensional datasets.
I am interested in statistical problems in genomics. To pursue this interest I
established a fruitful collaboration with Dr. McManus and his research laboratory.
Professor McManus is the Co-Director of iCAPTURE and the Director of the Cardiovascular
Research Laboratory and the Cardiovascular Registry, Department of Pathology and
Laboratory Medicine. The exciting project entitled "Better Biomarkers of Acute and
Chronic Allograft Rejection" recently obtained $9.1 million of funding over three
years. This project will generate very interesting statistical problems as well as
financial support for several Statistics graduate students and one or two postdoctoral
fellows.

4. New Statistical Procedures


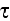 -Estimates: Victor Yohai and I introduced the class of robust
-Estimates: Victor Yohai and I introduced the class of robust 
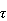 -estimates.
We defined these estimates for the case of linear regression. Now
-estimates.
We defined these estimates for the case of linear regression. Now 
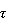 -estimates
have also been defined for multivariate location, orthogonal regression, principal
component, etc.
-estimates
have also been defined for multivariate location, orthogonal regression, principal
component, etc. 
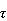 -estimates can attain breakdown point of
1/2 and arbitrary high efficiency at the "target" model.
-estimates can attain breakdown point of
1/2 and arbitrary high efficiency at the "target" model.

Orthogonal Regression M-Estimates: I defined these
estimates and studied their robustness properties.

Image Enhancement: Jean Meloche and I
proposed a generally applicable, non-parametric method to enhance and restore binary
images.

Robust (Fast) Bootstrap: Matias Salibian
and I developed a new bootstrap method to quickly estimate the variability of some
computational intensive robust regression estimates. Our robust bootstrap is not only
several orders of magnitude faster than classical bootstrap but also gives more stable and
reliable variance estimates in the presence of outliers and data contamination.

Linear Grouping Algorithm (LGA): together
with collaborators (Stefan Van Aelst, Steven Wang and Rong Zhu) we proposed a new approach
to clustering where items following similar linear relationship are grouped together.

CLUES: together with collaborators (Steven
Wang and Weiliang Qiu) we proposed a new approach to clustering based in k-near neighbors
averaging. Iteratively, each point is replaced by its local average and the procedure is
continued to convergence.

Pairwise Correlation Matrices: together
with collaborators (Ricardo Maronna and Fatemah Alqallaf ) we proposed several robust
correlation/covariance estimates based on pairwise operations. Two of these methods
(pairwise QC and pairwise GK) are now available in the Splus 6.1 robustness library.
STUDENTS AND TRAINEES

Post-Doctoral Fellows

| Name |
Supervisor |
Co- |
Date |
Funding |
|
|
Supervisor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| N. Le |
J. Zidek |
R. Zamar |
1988-1989 |
NSERC Operating |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| J. Adrover |
R. Zamar |
|
1999-2000 |
FOMEC (Argentina) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| M. Salibian |
R. Zamar |
|
2000-2001 |
PIMS & MathSoft Inc. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| S. Wang |
R. Zamar |
R. Ng |
2001-2002 |
PIMS & Insightful Co. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| R. Zhu |
R. Zamar |
R. Ng |
2002-2003 |
PIMS & iCapture |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| G. Cohen |
R. Zamar |
R. Ng |
2004- |
iCapture |
|
|
|
|
|
| G. Willems |
M. Salibian |
R. Zamar and H. Joe |
2005-2006 |
PIMS PDF |
|
|
|
|
|

Ph.D. Students

| Name |
Supervisor |
Co- |
Thesis Title |
Institution |
|
|
Supervisor |
|
|
| J.R. Berrendero |
R. Zamar |
J. Romo |
Contribuciones a la |
Estadistica |
|
|
|
teoria de robustez |
U. Carlos III |
|
|
|
respecto al sesgo (1996) |
Madrid-Spain |
| Matias Salibian |
R. Zamar |
|
Contributions to the |
Statistics |
|
|
|
theory of robust |
UBC |
|
|
|
inference (2000) |
|
| Ed Knorr |
R. Ng |
R. Zamar |
Outliers and data mining: |
Computer |
|
|
|
Finding exceptions in data |
Science |
|
|
|
(2002) |
UBC |
| Fatmah Alqallaf |
R.Zamar |
R. Ng |
A new contamination |
I.A.M. |
|
|
|
model for robust estimation |
UBC |
|
|
|
with large high-dimensional |
|
|
|
|
data (2003) |
|
| Jafar Khan |
R. Zamar |
S. Van Aelst |
Robust Linear Model Selection... |
Statistics, UBC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Mike Danilov |
R. Zamar |
|
|
Statistics, UBC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| M. Ruiz |
R. Zamar |
G. Boente |
|
Mathematics |
|
|
|
|
S.Luis, Argentina |
|
|
|
|
|
| M. Podder |
R. Zamar |
W. Welch |
|
Statistics, UBC |
|
|
Scott Tebbutt |
|
|
|
|
(iCAPTURE) |
|
|
| G. Yan |
W. Welch |
R. Zamar |
|
Statistics, UBC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Master Students

| Name |
Supervisor |
Co- |
Thesis Title |
Institution |
|
|
Superv. |
|
|
| Z. Patak |
R. Zamar |
|
Robust principal |
Statistics |
|
|
|
component analysis via |
UBC |
|
|
|
projection pursuit (1990) |
|
| S. Ferguson |
R. Zamar |
D. Ludwig |
Spatial estimation: the |
IAM |
|
|
|
geostatistical point of view |
UBC |
| R. White |
R. Zamar |
|
The detection and testing |
Statistics |
|
|
|
of multivariate outliers (1992) |
UBC |
| E. Rainville |
R. Zamar |
|
A comparison between |
Statistics |
|
|
|
several one-step M-estimates |
UBC |
|
|
|
of location and dispersion |
|
|
|
|
in the presence of a nuisance |
|
|
|
|
parameter (1996) |
|
| ManPo Lai |
R. Zamar |
J. Liu |
Robust test on equality |
Statistics |
|
|
|
of variances (1997) |
UBC |
| M. Ruiz |
R. Zamar |
|
Curvas de Estimacion |
U. Cordoba |
|
|
|
(2002) |
Argentina |
| J. Khan |
R. Zamar |
|
Globally robust inference |
Statistics |
|
|
|
for simple linear regression |
UBC |
|
|
|
with repeated median slope |
|
|
|
|
estimator (2002) |
|
| J. Chilson |
A. Wagner |
R.Ng and R. Zamar |
Parallel Computation of High |
Comp. Sce. |
|
|
|
Dimensional Robust Corr. |
UBC |
|
|
|
and Cov. Matrices (2004) |
|
| R. Zhang |
L. Lakshmanan |
R. Zamar |
Extracting XML Data from |
Stats. - UBC |
|
|
|
HTML Repositories (Exp. 2004) |
|
| Michael Regier |
R. Zamar |
M.C. Barroetavena |
Generalized Correlation |
Statis. UBC |
|
|
|
|
|
PUBLICATIONS

- Tomal, J.H. Welch, W.J. and Zamar, R.H. (2016) "Exploiting Multiple Descriptor Sets in QSAR Studies" Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 56 (3), pp 501 - 509
- Zhang, H., Leung, A. and Zamar, R.H. (2016) "Robust sparse hierarchical clustering. Submitted.
- Kondo, Y., Salibian-Barrera, M. and Zamar, R.H. (2016). "RSKC: An R Package for a Robust and Sparse K-means Clustering Algorithm". To appear in the Journal of Statistical Computing
- Leung, A., Zhang, H. and Zamar, R.H. (2016) "Robust regression estimation and inference in the presence of cellwise and casewise contamination". Computational Statistics and Data Analysis vol 99, 1-11.
- Tomal, H. W.J., Welch, W and Zamar, R.H. (2015). "Ensembling classification models based on phalanxes of variables with applications in drug discovery". The Annals of Applied Statistics 2015, Vol. 9, No. 1, 69-93.
- Agostinelli, C., Leung, A., J. Yohai, V.J., Zamar, R.H. (2015). Robust estimation of multivariate location and scatter in the presence of cellwise and casewise contamination. Test, 24, 441-461
- Agostinelli, C., Leung, A., J. Yohai, V.J., Zamar, R.H. (2015). Rejoinder on: Robust estimation of multivariate location and scatter in the presence of cellwise and casewise contamination. Test, 24, 441-461
- Zhang, H. and Zamar, R.H. (2013). Discussion of "How to Find an Appropriate Clustering for Mixed Type Variables with Application to Socio Economic Stratication" by Christian Hennig and Tim F. Liao. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series C (Applied Statistics), 62(3), 362-363.
- Zhang, H. and Zamar, R.H. (2013). "Least Angle regression for model selection", Advanced Review in WIREs Comput Stat 2013. doi: 10.1002/wics.1288. 2013
- Van Aelst, S, Willems, G. and Zamar, R.H.(2013).
"Robust and efficient estimation of the residual scale in linear regression", Journal of Multivariate Analysis 116, 278--296
- Pena, D., Viladomat, J. and Zamar, R.H. "Nearest-neighbours median cluster algorithm". Statistical Analysis and Data Mining 349-362. (2012)
- Cohen Freue, G.V., Ortiz-Molina, H. and Zamar, R.H. (2013). "A natural robustication of the classical instrumental variables estimator". Biometrics, 2013 . Sep; 69(3):641-50. doi: 10.1111/biom.12043. Epub 2013 Jul 19.
- Danilov, M., Yohai, V.J. and Zamar, R.H. (2012). "Robust estimation of multivariate location and scatter in the presence of missing data", Journal of the American Statistical Association, vol. 107(499), pages 1178-1186.
- Boente, G., Ruiz, M. and Zamar, R.H. (2012). "Bandwidth choice for robust nonparametric scale function estimation". Computational Statistics and Data Analysis vol. 56, 6, 1594-1608.
- Yan, G., Welch, W.J. and Zamar, R.H. (2010) Model-Based linear clustering, Can. J. of Statistics,
Vol. 38, No. 2, 2010, Pages 1-22. paper
-
Pena, D., Zamar, R.H. and Yan, G. (2008). "Bayesian likelihood robustness in
linear models". To appear in J. of Statistical Planning and Inference. ;
paper
-
Garcia-Escudero, L.A., Gordaliza, A., San Martin, R., Van Aelst, S.,
and Zamar, R.H. (2009). " Robust Linear Clustering", Journal of the Royal
Statistical Society B, 71 (2), 1-18.
paper
-
Ghement, R.I., Ruiz, M. and Zamar, R.H. (2008)."Robust Estimation of Error Scale
in Nonparametric Regression Models". J. of Statist. Planning
and Inference, 138, 3200-3216.
paper
- Alqallaf, F., Van Aelst, S.V., Yohai, V.J. and Zamar, R.H. (2009)
"Propagation of Outliers in Multivariate Data".
The Ann. of Statist., 37, 311-331.
paper
-
Salibian-Barrera, M., Willems, G. and Zamar, R.H. (2008). "The fast-Tau-estimator
for regression". Computational and Graphical
Statistics, Vol. 17, 659-682.
paper
-
Gabriela V. Cohen Freue, Zsuzsanna Hollander, Enqing Shen, Ruben H. Zamar, Robert Balshaw, Andreas Scherer, Bruce McManus, Paul
Keown, W. Robert McMaster, and Raymond T. Ng (2007)."MDQC: A New Quality
Assessment Method for Microarrays Based on Quality Control
Reports". Bioinformatics 23 (2007) 3162-3169. paper
- Khan, J.A., Van Aelst, S., and Zamar, R.H. (2007), "Robust Linear Model Selection Based on Least Angle Regression,"
Journal of the American Statistical Association,
Vol. 102, No. 480, pp.1289-1299.
paper &
software
- Podder, M., Welch, W.J. Zamar, R.H. and Tebbutt, S.J.
(2006). " Dynamic Variable Selection in SNP Genotype Autocalling
from APEX Microarray Data", BMC Bioinformatics 2006, 7:521
paper
- Willems, G., Joe, H. and Zamar, R.H. " Diagnosing multivariate outliers detected by
robust estimators".
paper
- Cohen-Freue, G., Ortiz-Molina, H. and Zamar, R.H.
"A Natural Robustification of the Ordinary Instrumental
Variables Estimator". Submitted to Biometrics
"A robust instrumental variables estimator". Submitted 2006
paper
- Khan, J., Van Aelst, S. and Zamar, R.H. (2007). "Building a robust linear model with forward
selection and stepwise procedures." Computational Statistics &
Data Analysis, Volume 52, Issue 1, 239-248.
paper
- Danilov, M., Ng, R., Yohai, V.J. and Zamar, R.H. "Robust Regression by Cone
Reweighting". In preparation.
-
Chilson, J., Ng R., Wagner, A., and Zamar, R.,"Parallel Computation of
High Dimensional Robuts Correlation and Covariance Matrices".
Algorithmica, Special Issue on Coarse Grain Computation,
Springer New York, Vol. 45, No. 3, pp. 403-431, 2006.
paper
- Zhang, R.Y., Lakshmanan L.V.S. and Zamar, R.H. (2004). "Extracting XML Data from HTML
Repositories", SIGKDD Newsletter, Volume 6, Issue 2, pg 5-13.
paper
- Wang X., Qiu W. and Zamar, R.H. (2007). "CLUES: A non parametric clustering method based on
local shrinking". Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, Volume 52,
Issue 1, 286-298
paper
- Van Aelst, S., Wang, X., Zamar, R.H. and Zhu, R. (2006). "
Linear Grouping Using Orthogonal regression," Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 50, 1287-1312."
paper
package
talk
- Chilson, J., Ng, R., Wagner, A. and Zamar, R. (2004). "Parallel computation of high
dimensional robust correlation and covariance matrices", Proceedings of the ACM
SIGKDD, 533-538.
paper
- Berrendero, J.R. and Zamar, R.H. (2004). "A note on the uniform asymptotic
normality of location M-estimates". To appear in Metrika.
- Yohai, V. and Zamar, R.H. (2004). "Robust non-parametric inference for the
median". Ann. of Statist., Vol. 32, No. 5, 1841--1857.
- Salibian-Barrera, M. and Zamar, R.H. (2004). "Uniform asymptotic for robust
location estimates when scale is unknown". Ann. of Statist. Vol. 32, No. 4,
1434--1447.
- Adrover J. and Zamar, R.H (2004). "Bias robustness of three median-based regression
estimates", J. of Statist. Planning and Inference. 203-227.
paper
- Adrover, J., Salibian, M. and Zamar, R.H. (2004). "Globally robust inference for
location and the simple linear regression model". J. of Statist. Planning and
Inference, 119, 353-375.
paper
- Adrover, J., Berrendero, J.R., Salibian, M. and Zamar, R.H. "Globally robust
inference". (2002). Estadistica, 54, 127-161.
- Maronna, Ricardo and Zamar, R.H. (2002). "Robust multivariate estimates for high
dimensional data sets". Technometrics, 44 (4) 307-317.
- Aqallaf, F.A., Konis, K..P., Martin, R.D. and Zamar, R.H. (2002). "Scalable robust
covariance and correlation estimates for data mining" . Proceedings of the Seventh
ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data, Mining, Edmonton,
Alberta 14-23.
paper
- Svartz, M., Yohai, V.J., and Zamar, R.H. (2002). "Optimal bias robust M--estimates
of regression", submitted for the proceedings of the International Conference on L1
and Related Methods, Neuchatel, Switzerland, 191- 200
- Park, J. and Zamar, R.H. (2001). "The detection and testing of multiple outliers in
linear regression". Bulletin of the International Statistical Institute. 53rd
Contributed Papers -- Tome LIX, Book 1 -- Seoul, Korea. 473-474.
- Yohai, V.J. and Zamar, R.H. (2001). "A review of recent robust inference: an
approach based on maxbias". Bulletin of the International Statistical Institute. 53rd
Session Proceedings -- Seoul, Korea. 505-508.
- Knorr, E., Ng, R. and Zamar, R.H. (2001). "Robust space transformation for distance
based operations". Proceedings of the Seventh ACM SIGKDD International Conference on
Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, California, 126-135.
- Salibian, M. and Zamar, R.H. (2002). "Bootstrapping robust estimates of
regression". The Ann. of Statist. 30, 556-582 .
- Berrendero, J.R. and Zamar, R.H. (2001). "The maxbias curve of robust regression
estimates". The Ann. of Statist. 29, No. 1, 224-251
- Fraiman, R., Yohai, V.J. and Zamar, R.H. (2001). "Optimal robust m-estimates of
location". The Ann. of Statist. 29, No. 1, 194 - 223.
- Heckman, N. and Zamar, R.H. (2000). "Comparing the shape of regression functions".
Biometrika. 87, 1, pp. 135-144.
paper
- Berrendero, J.R. and Zamar, R.H. (1999). "Global robustness of location and
dispersion estimates". Statist. and Probability Letters, 44, 63-72.
- Ferretti, N, Kelmansky, D., Yohai, V.J. and Zamar, R.H. (1999). "A class of locally
and globally robust regression estimates". J. Amer. Statist. Ass. 94, 174-188
- Berrendero, J., Mazzi, S., Romo, J. and Zamar, R.H. (1998). "On the Explosion Rate
of Maxbias Functions". appear Can. J. of Statist., 26, 333-351
- Justel, A., Pena, D. and Zamar, R.H. (1997). "A multivariate
Kolmogorov-Smirnov test of goodness of fit". Stat. and Probab. Letters, 35, 251-59
- Pena, D. and Zamar, R.H. (1997). "A simple diagnostic tool for local prior
sensitivity". Statist. and Probab. Letters, 36, 205-212.
- Yohai, V.J. and Zamar, R.H. (1997). "Optimal locally robust M-estimates of
regression". Journal of Statist. Planning and Inference, Vol. 66, 2, 309-323.
- Pena, D. and Zamar, R.H. "Bayesian Robustness: An Asymptotic Approach".
(1996). In Robust Statistics, Data Analysis, and Computer Intensive Methods (H. Rieder,
Ed.). Springer Lecture Notes in Statistics #109, 361- 374.
- Li, B. and Zamar, R.H. (1996). "M-estimates of regression when the scale is unknown
and the error distribution is possibly asymmetric: a minimax result". Can. J. of
Statist., Vol. 24, 2, 193-206.
- Zamar, Ruben H. "Estimacion Robusta". With discussion. (1994). Estadistica
Espanola. Vol. 36, No. 137, 317-387
- Meloche, J. and Zamar, R.H. (1994). "Binary-image restoration". Can. J. of
Statist., Vol 22, 4, 335-355.
- Maroma, R., Yohai, V.J. and Zamar, R.H. (1993). "Bias-robust regression estimation:
A partial survey". In New Directions in Statistical Data Analysis and Robustness. S.
Morgentaler, E. Ronchetti and W.A. Stahel (Ed.), Birkhauser, Basilea, 157-176.
- Yohai, V.J. and Zamar, R.H. (1993). "A minmax-bias property of the least
Alpha-quantile estimates". The Annals of Statistics, 21, No. 4, 1824-1842.
- Martin, R.D. and Zamar, R.H. (1993). "Bias robust estimates of scale". The
Annals of Statistics, 21, No. 2, 991-1017 .
- Martin, R.D. and Zamar, R.H. (1993). "Efficiency constrained bias robust estimation
of location". The Annals of Statistics, 21, No. 1, 338-354,.
- Zamar, R.H. "Bias robust estimation in orthogonal regression". The Annals of
Statistics, 20, 1875-1888, (1992).
- Le, N. and Zamar, R.H. (1992). "A global test for effects in 2k factorial designs
without replicates". Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation, 41, 41-54,.
- Yohai, V.J., Stahel, W. and Zamar, R.H. (1991). "A procedure for robust estimation
and inference in linear regression". In: Directions in Robust Statistics and
Diagnostics, Part II, W. Stahel and S. Weisberg (Eds), Springer-Verlag, 365-374, .
- Yohai, V.J. and Zamar, R.H. (1991). "Bounded influence estimation in the
errors-in-variables model". In: Statistical Analysis of Measurement Error Models and
Applications, Philip J. Brown and Wayne A. Fuller (Editors), Contemporary Mathematics,
112, 243-248,.
- Li, B. and Zamar, R.H. (1991). "Min-max asymptotic variance when scale is
unknown". Statistics and Probability Letters, 11, 139-145,.
- Zamar, R.H. (1990). "Robustness against unexpected dependence in the location
model". Statistics and Probability Letters, 9, 367-374,.
- Martin, R.D., Yohai, V.J. and Zamar, R.H. (1989). "Min-max bias robust
regression". Annals of Statistics, 17, 1608-1630, .
- Martin, R.D. and Zamar, R.H. (1989). "Asymptotically min-max bias-robust
M-estimates of scale for positive random variables". Journal American Statistical
Association 84, 494-501,.
- Zamar, R.H. "Robust estimation in the errors in variables model" (1989).
Biometrika, 76, 149-60.
- Yohai, V.J. and Zamar, R.H. (1988). "High breakdown-point estimates of regression
by means of the minimization of an efficient scale". Journal American Statistical
Association, 83, 406-413..

Recent Invited Talks

- Invited speaker at the Workshop in Honor of Victor Yohai, Madrid, Spain, October, 2006.
- Invited speaker at ICORS 2006, Lisbon, Portugal, July, 2006.
- Invited speaker, 25th European Meeting of Statisticians , Oslo July 24-28 2005. Invited Session "IS16 - NEW DIRECTIONS IN ROBUST
STATISTICS".
- "Robust Methods and Data Mining". Workshop on Data Mining Methodology and
Applications at The Fields Institute, Toronto, October 28-30, 2004
- Keynote speaker (opening talk) at the Workshop on Robustness for High-Dimensional Data,
Sponsored by the European Science Foundation, Vorau, Austria, May 5-8, 2004.
- Keynote speaker (opening talk) at the CASCON 2003 Workshop on Categorical Data Analysis.
Toronto, November, 2003.
- "Pair-wise approach to Scatter Matrix Estimation", International Conference on
Statisitics, Combinatorics and Related Areas, Maine, USA, October 2003.
- "Robust Model Selection", ICORS 2003, Antwerp, July 13-18, 2003.
- "A new model for data contamination", SCC, Invited session on Data Mining,
Halifax, June 8-12, 2003.
- "Robust Bootstrap". 24th European Meeting of Statisticians. Prague, August
19-23, 2002.
- "Optimally robust regression M-estimates", Fourth International Conference on
Statistical Data Analysis Based on L1 Norm and Related Methods, Newchatel, Switzerland,
August 4-9, 2002.
"A Review of Recent Robust Inference: An Approach Based on
Maxbias", 53rd International Statisitical Institute, Seoul, Korea, August 2001.
- "Three Median based regression estimates", Minerva Conference on Robust
Statistics, B. Aires, Argentina, 2001.
- "Non-Parametric and Robust Confidence Intervals", International Conference on
Robust Statistics (ICORS 2001), Vorau, Austria, July 2001.
- "Robust covariance for very large datasets", Joint Statistical Meetings,
Atlanta, USA, August 2001
- "Comparing the shape of regression functions", V ICSA International
Conference, Hong Kong, China, August 2001.

Recent Research Support
| Grant/Contract |
Funding Agency/ |
Amount |
Period |
Comments |
|
Company |
(per year) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Discovery Grant |
NSERC |
32,000 |
2004-2009 |
PI: R. Zamar |
|
|
|
|
|
| Operating Grant |
NSERC |
22,500 |
2000-04 |
PI: R. Zamar |
|
|
|
|
|
| Toward |
MITACS |
150,000 |
2002-04 |
Leader: R. Ng |
| Interactive |
& Industrial |
|
|
PI's: R. Zamar and |
| Data Mining (grant) |
Partners |
|
|
4 other people |
|
|
|
|
|
| Usable Robust |
MathSoft Co. and |
42,000 |
2000-01 |
PI: R. Zamar |
| Procedures |
PIMS |
|
|
PDF: M. Salibian |
| (contract) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Data Mining |
Insightful Co. and |
42,500 |
2001-02 |
PI's: R. Zamar |
| (grant) |
PIMS |
|
|
and R. Ng |
|
|
|
|
PDF (S. Wang) |
| Bioinformatics |
IBM, iCAPTURE |
45,000 |
2002-03 |
PI's: R. Zamar and R. Ng |
|
and PIMS |
|
|
PDF (Rong Zhu) |
| Equipment Grant |
NSERC |
45,000 |
2003-04 |
PI: R. Zamar |
|
|
|
|
|
| Interactive |
Teaching and |
50,000 |
2003-04 |
PI: R. Zamar |
| Learning |
Learning |
|
|
|
| Tools (grant) |
Enhancement |
|
|
|
|
Fund (UBC) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

EDITORIAL ACTIVITIES

- Associate Editor, Annals of Statistics 2004-2007
- Associate Editor, Test since 1998.
- Associate Editor, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1991-93.
- Reviewer for the Mathematical Reviews since 2000.
- Member of KDD-2003 Program Committee, Washington, DC, U.S.A.
- Co-Editor of the Proceedings of ICORS 2003, Antwerp, Belgium.
- Co-Editor of the Proceedings of ICORS 2001, Vorau, Austria.

CONFERENCE ORGANIZATION

- Co-organizer (with Stefan Van Aelst, Ghent University, Belgium) of the Focused Research
Group on Robust Analysis of Large Data Sets. Banff International Research Station. June 5
- 19, 2004.
- Member of Scientific Committee, Symposium on Data Mining, IMS - mini meeting, University
of Ghent, May 2004.
- Member of Scientific Committee of ICORS 2003, June 2003, Antwerp, Belgium.
- Co-organizer (with Arnold Stromberg) of the "Workshop on Robust Computational
Procedures 2002" . This workshop, held at PIMS, received funding from NSF and PIMS.
- Co-organizer (with Ursula Gather and Chris Field) of ICORS 2002, June 2002, Vancouver,
Canada. This conference received funding from PIMS and the Minerva Research Foundation.

AWARDS

- "Best Paper Award" International Conference on Knowledge
Discovery and Data Mining 2001 (KDD2001) San Francisco, jointly with Ed Knorr and Raymond
Ng.
- "2001/02 Science Research Achievement Awards", Faculty of
Science, UBC.

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

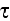 -Estimates: Victor Yohai and I introduced the class of robust
-Estimates: Victor Yohai and I introduced the class of robust 
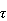 -estimates.
We defined these estimates for the case of linear regression. Now
-estimates.
We defined these estimates for the case of linear regression. Now 
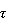 -estimates
have also been defined for multivariate location, orthogonal regression, principal
component, etc.
-estimates
have also been defined for multivariate location, orthogonal regression, principal
component, etc. 
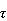 -estimates can attain breakdown point of
1/2 and arbitrary high efficiency at the "target" model.
-estimates can attain breakdown point of
1/2 and arbitrary high efficiency at the "target" model.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()